Animal Cell Immersed In Hypotonic Solution / Red Blood Cells In Hypotonic Solution - It is commonly used when describing the response of cells immersed in an external solution.. What happens to animal cells if they are put in a hypotonic. How do red blood cells react in a hypotonic solution? What happens to an animal cell in a hypotonic solution? Also, with the help of the science teacher or an adult, make a microscope slide with the. Hypotonic solutions increase the pharmacologic activity and absorption of nasally administered drugs vs solutions of increased osmolarity.
When they are in a hypotonic solution, water can enter the cell through osmosis. A solution which have high concentration as compared to the semple we applied. Hypotonic solution animal cell hypotonic solution plant cell selectively permeable membrane facilitated diffusion passive transport cell membrane. Like osmotic pressure, tonicity is influenced only by solutes that cannot cross the membrane, as only these exert. Not animal examples (slugs) please, just make if a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, water will be attracted to the environment and leave the of a cell being immersed in a solution in the cell is this magenta circle that's the cellular membrane.

Spherocytes are osmotically fragile cells that rupture more easily in a hypotonic solution than do normal rbcs.
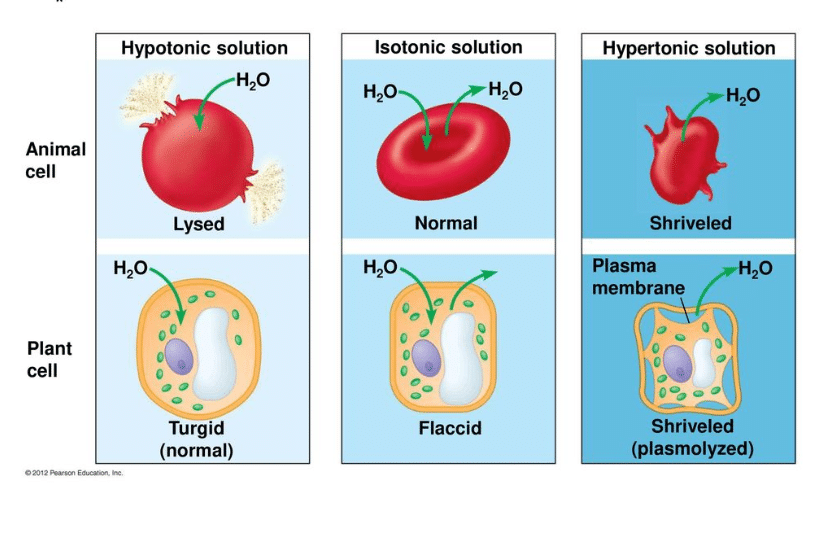
Cells placed in a hypotonic solution will take in water across their membranes until both the external solution and the cytosol are isotonic. And covered by a selectively permeable cell membrane which freely allows movement of solvent. .a hypotonic, a hypertonic, or an isotonic solution? A hypotonic environment (or solution) means that there is a lower concentration of solute in the environment that there is in the cell. What accounts for the difference in outcomes between animal cells and plant. Imagine you and two other people are waiting for an elevator in the lobby of a building. A plant cell immersed in hypotonic solution. When they are in a hypotonic solution, water can enter the cell through osmosis. Also, with the help of the science teacher or an adult, make a microscope slide with the. Basic cellular components of plant cells and animal cells, especially the plasma membrane. Hypertonic solution because it causes the water to leave the cell by the osmosis. Osmosis through a animal cell: Cells are made up of water and solutes suspended or dissolved in it.
To prevent crenation or hemolysis, an animal cell must be placed in an isotonic solution such as 0.9% (m/v) nacl or 5.0% (m/v) glucose. Animals and plant cells have a selectively permeable membrane around them that lets some chemicals pass (like a hypotonic solution has a lesser solute concentration than that in the cell. Hypertonic solution because it causes the water to leave the cell by the osmosis. Animal cells tend to do best in an isotonic environment, where. A hypotonic environment (or solution) means that there is a lower concentration of solute in the environment that there is in the cell.

What happens to an animal cell in a hypotonic solution?
Basic cellular components of plant cells and animal cells, especially the plasma membrane. Animals and plant cells have a selectively permeable membrane around them that lets some chemicals pass (like a hypotonic solution has a lesser solute concentration than that in the cell. When they are in a hypotonic solution, water can enter the cell through osmosis. An animal cell immersed in hypertonic solution. This allows the plant to support itself. The given diagram shows the appearance of plant cell immersed in a. A plant cell immersed in hypotonic solution. A solution which have low concentration in comparison with sample. red blood cell example pg 70 what is effect of immersing an animal cell in a hypertonic or hypotonic solution? Maintain cell shape and prevents cells from lysing in hypotonic enviroments. There is more solute inside the cell than in the solution surrounding the cell. Hypotonic solution animal cell hypotonic solution plant cell selectively permeable membrane facilitated diffusion passive transport cell membrane. When a plasmolysed plant cell is immersed in a hypotonic solution again…
Large plants and fungi control the environment around their cells, helping ensure the environment is always a hypotonic solution, compared to the cells. In these conditions, an animal cell would burst, but because plant cells have cell. All animals were catheterized from the femoral artery and vein, and pressure transducers were 3.1. When a plant is immersed in a hypertonic solution, water leaves the plant cell and it shrivels up. A red blood cell is placed into each of the following solutions.
When they are in a hypotonic solution, water can enter the cell through osmosis.
Cells placed in a hypotonic solution will take in water across their membranes until both the external solution and the cytosol are isotonic. Secondary cell walls (scws) are a key component for mediating mechanical strength and stiffness in this paper, we study the structure and biomechanics of cultured plant cells during the cellular prior to triggering differentiation, cells in hypotonic pressure conditions are significantly stiffer than cells in. A solution which have low concentration in comparison with sample. Plants have evolved to absorb water and are healthiest when their cells are turgid, or full of water. The cell could rupture in a process known as cytolysis. There is more solute inside the cell than in the solution surrounding the cell. Basic cellular components of plant cells and animal cells, especially the plasma membrane. When a plasmolysed plant cell is immersed in a hypotonic solution again… What happens to animal cells if they are put in a hypotonic. What happens to plant cells when placed in a hypotonic solution? Cell immersed in hypertonic solution cell immersed in hypotonic solution osmosis, con't contractile vacuole. Isotonic solution a solution which has the same water potential than another solution hypotonic solution a solution which has a higher 3. Hypotonic solution is a solution which, contains lesser solute concentration.